What is augmented reality ?
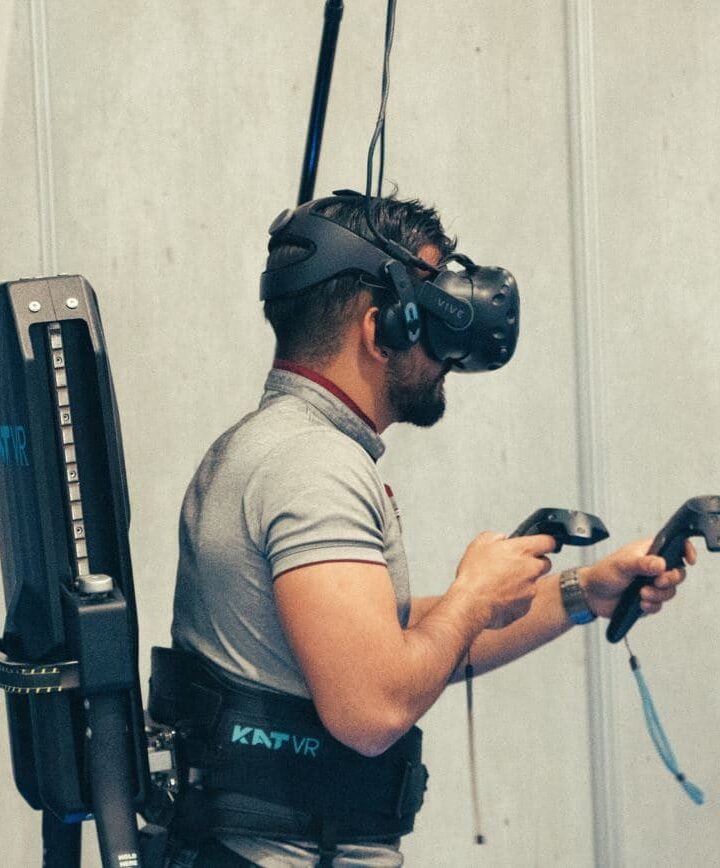
Augmented reality, or AR for short, is a technology that consists of superimposing virtual visual or auditory elements on the real world, using a multimedia device. In concrete terms, AR is based on the recording of reality by a device and the addition, in real time, of 3D elements, which are superimposed on the real world. In factories, for example, these virtual additions appear in the worker’s field of vision using special glasses.
What is the difference with virtual reality?
Augmented reality is often accompanied by the notion of virtual reality, also called VR. Virtual reality is a computer-generated simulation of an alternative world or reality. While augmented reality augments the real scene, virtual reality creates fully immersive virtual environments.
The two technologies complement each other and are used in the 4th industrial revolution : Industry 4.0.
Why use augmented reality in industry?
AR is widely used in Industry 4.0 because it brings many benefits to the industry, and allows the optimisation of different sectors. AR is particularly useful in the following areas :
- Manufacturing ;
- Industrial maintenance
- Logistics;
- Marketing and sales;
- Workplace safety;
- Training.
Let’s take a closer look at the benefits of augmented reality through examples.
-
Augmented reality for assembly operations:
Often, to understand assembly procedures, companies use PDFs or paper guides. Augmented reality simplifies this understanding by presenting information directly in the user’s field of vision.
Augmented reality is particularly relevant in jobs where the number of sequences and complexity is high. For this reason, it is used in aeronautics, notably in the Boeing project, on the assembly operations carried out on the parts that will support the engines of the 737 MAX. It is the first of its kind to be assembled using augmented reality. Augmented reality reduces the need for advanced technical expertise and, at the same time, the mental burden on the employee in his daily work. It is very useful for replacing assembly guides and improving maintenance and inspection of parts.
-
Augmented reality: the future of education
AR is also increasingly being used in the education and vocational training sector.
By making learning more engaging and fun, it helps students acquire, process and remember information more effectively. Indeed, AR has the potential to replace paper-based learning materials with portable and less expensive ones. It can also improve collaboration skills by introducing interactive lessons where students are involved.
In the professional world, it can, for example, reproduce field conditions to help workers master the practical skills required for a certain job.
-
Augmented reality to help with industrial breakdowns
Thanks to many innovations, augmented reality can now be a powerful troubleshooting solution. When a machine breaks down, AR can be used to connect the remote expert with a technician at the breakdown site. Using augmented reality glasses, a person in front of the machine can transmit a video to the expert. By interacting with the images, the expert can highlight the elements to be repaired, without having to go to the site.
-
Augmented reality in sales and marketing
In the sales sector, AR can provide consumers with a new immersive experience. For example, instead of showing a sales video, the item could be presented in augmented reality. This is particularly relevant in the automotive sector. Using an augmented reality headset, the salesperson could offer customers a realistic immersion in the car they want, to test all its features.
-
Almost endless possibilities
There are many examples of augmented reality being used. This technology is a growth driver within the industry and many companies describe it as a must-have. Therefore, whatever your field of expertise, it is imperative to learn about this technology, in order to seize the opportunities it can offer you.
Written by Emma Guignard