Regulatory Compliance and Financial Performance: The Strategic Edge
FAA Regulatory Alignment and Part 145 Compliance
In the United States, maintaining an FAA Part 145 repair station certificate requires uncompromising oversight of personnel and procedures. Real-time scheduling systems integrate FAA regulatory requirements directly into the production flow. By automating the verification of 14 CFR Part 65 certifications, the system ensures that only appropriately rated mechanics perform and sign off on specific maintenance tasks. This digital oversight mitigates the risk of civil penalties and ensures that the MRO facility remains “audit-ready” at all times, maintaining the highest levels of safety and airworthiness.
The ROI of Digital Twin Implementation in Shop Floor Management
Investing in a Digital Twin for MRO operations yields a measurable Return on Investment (ROI) by eliminating hidden inefficiencies. Organizations implementing these holistic models typically observe:
- 15-25% Reduction in Labor Waste: By eliminating “search time” for parts and tools through real-time asset tracking and synchronized scheduling.
- Optimized Asset Utilization: Maximizing the occupancy of high-value hangar bays and specialized GSE (Ground Support Equipment).
- Reduced Holding Costs: Improved synchronization with the supply chain allows for Just-In-Time (JIT) parts delivery, reducing capital tied up in inventory.
Beyond immediate productivity gains, the Digital Twin provides a “sandbox” for predictive modeling. Facilities can simulate the impact of taking on new contracts or changing shift patterns before execution, drastically reducing the financial risk associated with operational scaling.
Conclusion: Transforming the Shop Through Intelligent Scheduling
Excellence in MRO no longer rests solely on technical skill, but on organizational intelligence. By adopting agile, real-time scheduling and Digital Twin technology, facilities transform operational constraints into competitive advantages. This evolution is the key to reducing costs, exceeding customer expectations, and securing long-term profitability in a demanding global aviation market.
Supply Chain and Repair Synchronization
Component wait time is the primary waste (Muda) identified in Lean Maintenance. Interconnecting scheduling with inventory management allows for adjusting job sequences based on the Estimated Time of Arrival (ETA) of critical components. The real-time system automatically reallocates resources to alternative tasks to maintain team productivity in the event of logistical delays.
Managing shortages and supply chain disruptions must rely on statistical methods and Material Requirements Planning (MRP) tools. These aim to anticipate stock-out risks as early as possible and establish safety stock levels.
However, given the highly stochastic nature of MRO operations, stock anticipation and sizing are not enough. It is therefore necessary to have an ultra-responsive, near-real-time scheduling system that reacts as quickly as possible to field realities.
Load Balancing and Stability (Heijunka)
Flow balancing prevents shop floor saturation and periods of inactivity. A high-performance scheduling engine analyzes heavy maintenance forecasts (C-Checks) to level them with line maintenance requirements. This approach reduces the reliance on overtime and limits the wear and tear on human capital.
Technological Breakthroughs and Research in Scheduling
Advanced Planning & Scheduling (APS) Systems
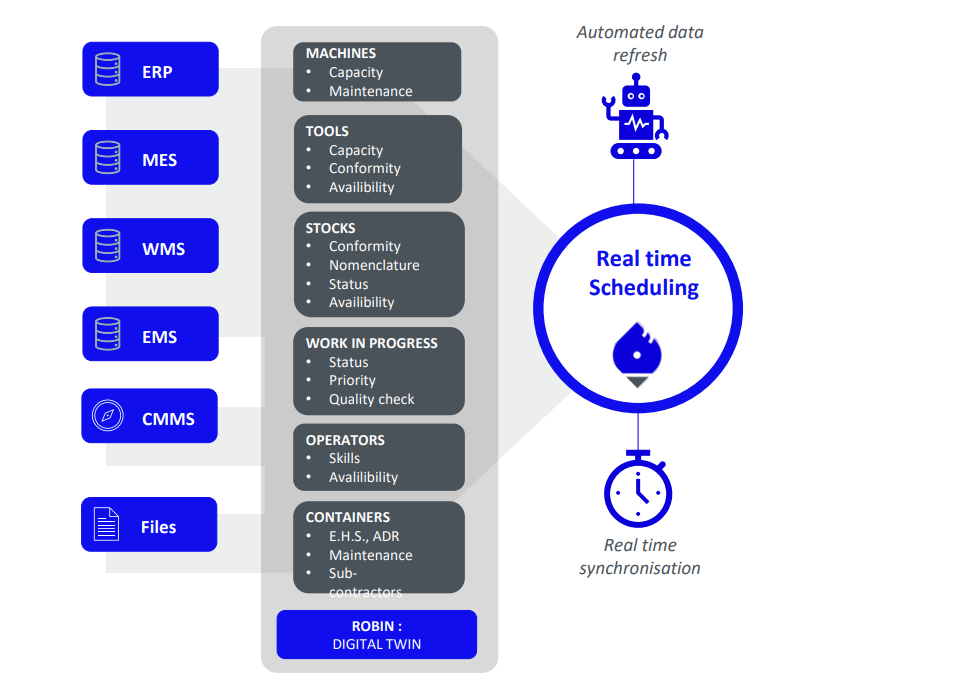
While the ERP manages transactional data, the APS provides the intelligence of movement. These solutions utilize calculation engines capable of processing thousands of combinatorial variables in seconds. The APS identifies the optimal scenario by arbitrating between delivery priorities and cost constraints.
Artificial Intelligence and Operations Research
The introduction of genetic algorithms and reinforcement learning enables a shift from reactive to predictive logic. Analyzing historical data allows systems to anticipate the probability of non-routine work in specific zones, thereby reserving a preventive buffer within the schedule.
Regulatory Framework and the Human Factor
Part-66 Compliance and Certification Management
In aviation, scheduling intrinsically integrates the regulatory dimension. Every intervention must be assigned to personnel holding the appropriate license (B1, B2, C). Automating this verification within the planning tool secures the Approval for Return to Service (RTS) and eliminates non-compliance risks.
Digital Certification Management: Integrating Matrix Skills Solutions
Interoperability Between Scheduling and Skill Management: The Mercateam and Zozio Model
The performance of real-time scheduling depends on the reliability of input data, particularly regarding skill availability. The emergence of platforms specialized in aptitude management, such as Mercateam or Zozio, is revolutionizing MRO by dynamically connecting the skill matrix to the production schedule. These tools map multi-skilling and ensure that every assigned resource possesses not only the hourly availability but, more importantly, the technical aptitude required for the task.
Automating Part-66 Compliance and Securing RTS
In aviation, strict adherence to EASA Part-66 (or 14 CFR Part 65 in the US) regulations is a non-negotiable constraint. Utilizing digital certification management software automates license verification (B1 for airframe/engine, B2 for avionics). By integrating these data flows directly into the scheduling engine, the system proactively blocks task assignments to any technician whose specific license or certification (high-altitude work, NDT, borescope) has expired. This synchronization between production and HR secures the Return to Service (RTS) and eliminates the risk of negative audits from oversight authorities.
Toward Predictive Training Planning
Beyond immediate execution, cross-referencing data from Zozio or Mercateam with forecasted workloads identifies capacity vulnerabilities. If the schedule detects a surge in C-Check visits for a specific fleet (such as Airbus A320neo or Boeing 737 MAX), the system alerts management to the need for refresher courses or Type Ratings. This approach transforms human resource management into a strategic lever for MRO industrial fluidity.
Conclusion: Intelligent Scheduling as a Competitive Driver
Operational excellence in MRO depends on organizational intelligence. Adopting agile, technology-driven scheduling transforms production constraints into strategic advantages. This approach is decisive for reducing operational costs and ensuring the sustainability of maintenance centers in a highly competitive aerospace market.
Discover how Zozio can redefine your MRO operations by exploring our platform, and join the revolution to transform maintenance processes and secure your TAT reliability.

